REVIEWS | PORCINE DISEASES
Introduction. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS), caused by a virus from the family Arteriviridae, is one of the most economically significant porcine diseases in many countries. The disease is mainly manifested by reproductive disorders in sows, i.e. abortions in late pregnancy, early or delayed farrowing, birth of weak or non-viable piglets, irregular estrus; pathologies in early and middle pregnancy are less often reported. Piglets and fattening pigs have respiratory distress syndrome: coughing, sneezing, dyspnea and stunted growth. In addition, infection with PRRS virus undermines respiratory immunity, which makes the infected pigs more susceptible to secondary infections and increases mortality in the herd. This review provides up-to-date information on the current laboratory diagnostic tools and recent data on specific PRRS prevention and gives information on the promising biotechnological platforms that can be used to design new-generation vaccines.
Objective. To consider and summarize modern approaches to diagnosis and prevention of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome.
Materials and methods. Scientific publications of foreign and domestic authors served as the material for the research.
Results. The paper presents nosological characteristics of the disease, explores distinctive features of its clinical manifestations and epizootiology; analyzes structure of the pathogen’s genome. This review describes and evaluates laboratory diagnostic techniques (both conventional and modern); currently available anti-PRRS vaccines and novel biotech platforms enabling to design safer and more effective next-generation vaccines. There are three major challenges in vaccine development at the current stage of PRRS pathogenesis research: insufficient understanding of immune protection mechanisms, the virus’s ability to induce negative regulatory signals for the immune system, and the pathogen’s high antigenic variability.
Conclusion. PRRS virus strains exhibit significant genetic and antigenic heterogeneity and frequently undergo recombination, which exacerbates the challenges of epizootiology, disease prevention, and control. Further in-depth study of host immune response characteristics, along with identification of T- and B-cell epitopes in the pathogen structure, will enable rational design of genetically engineered vaccines.
Introduction. Effective measures for African swine fever outbreak prevention and early detection are required in view of global spread of African swine fever, fatal viral hemorrhagic disease of domestic pigs and wild boars. Wild boar population managing and search for the wild boars died of African swine fever and being the virus source are considered priority measures for the disease control in wildlife.
Objective. Generalization of currently available knowledge about advanced technologies for the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) in combination with artificial intelligence-based methods in the wild.
Materials and methods. Analytical research methods including search in the following databases were used: PubMed, Springer, Wiley Online Library, Google Scholar, CrossRef, Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI), еLIBRARY, CyberLeninka.
Results. Potential of using unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) and artificial intelligence (neural network) for detection of wild boars and their remnants in the context of combating African swine fever is described in the review. The role of wild boars in the disease spread and the need for wild boar population regulation are discussed in detail. Also, the importance of timely wild boar carcass removal and use of modern technologies for wild boar population recording and its density estimation are underlined. Data on the use of drones equipped with various technical devices for study of large animal populations in the wild are analyzed, advantages and peculiarities of unmanned aerial vehicle use are indicated. Experience gained in using neural networks-based techniques for automatic processing of animal images acquired from drones is also summarized.
Conclusion. Artificial intelligence-integrated unmanned aerial vehicles appear to be a key tool for managing wild boar populations and the rapid detection of African swine fever dead wild boars that allows improvement of overall effectiveness of the measures taken against this disease.
REVIEWS | BOVINE DISEASES
Introduction. Bovine respiratory syncytial infection is widespread in all countries of the world, including the Russian Federation. The etiologic agent is Orthopneumovirus bovis, it belongs to the family Pneumoviridae, genus Orthopneumovirus. Cattle are the main reservoir of the virus.
Objective. This literature review aims to summarize and give analysis of the published data on clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and molecular epidemiology of the causative agent of bovine respiratory syncytial infection.
Materials and methods. The study is based on publications from the most authoritative domestic (eLIBRARY.RU) and foreign (Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed) sources, as well as the results of our own studies published in the literature.
Results. Animals of all ages are susceptible to the disease, the infection is most severe in calves under 6 months of age. The incidence of the herd is on average 60–80%. The nature of the infection varies from asymptomatic and mild to severe lower respiratory tract disease, including emphysema, pulmonary edema, interstitial pneumonia and bronchopneumonia, while the mortality rate among calves can reach 20%, and in adult animals the subclinical form is more often recorded. The virus has a powerful immunomodulatory effect. Severe damage to the respiratory tract is mediated mainly by hyperactivity of the immune response, and not by the replication of the virus itself. The virus increases the susceptibility of calves to secondary infections and promotes colonization of the lower respiratory tract by bacteria. Currently, ten genetic subgroups of the virus (I–X) have been identified using phylogenetic analysis of the nucleotide sequences of the G and N genes, between which there is a geographical correlation. In regions such as the Urals, Siberia, and the Republic of Kazakhstan, isolates of the virus of genetic subgroups II and III circulate among cattle.
Conclusion. The review presents current data on the etiology, pathogenesis features and clinical manifestations of bovine respiratory syncytial infection, as well as the genetic diversity of the pathogen in the world, in the Russian Federation and the Republic of Kazakhstan.
REVIEWS | FISH DISEASES
Introduction. With the decline in industrial salmon catches, fish hatcheries play a crucial role in replenishing stocks of these commercially valuable fish species. In aquaculture conditions, salmonids often demonstrate eye lesions, which reduce their adaptability in natural environments. Diagnosing these pathologies enables their classification by causative factors and development of therapeutic and preventive measures.
Objective. To search for and summarize scientific publications on ocular pathologies in salmonids at facilities engaged in industrial breeding, commercial farming or reproduction in Asia, America, Europe, and the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. A search for Russian- and English-language articles in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and eLIBRARY.RU databases was conducted. To prepare the review, 44 research papers published between 1975 and 2024 were used.
Results. The study demonstrates that eye lesions in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), brown trout (Salmo trutta), and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), such as non-parasitic cataracts (lens opacity), keratopathy (corneal opacity), and unilateral or bilateral exophthalmia (eye protrusion), are reported at fish hatcheries and aquaculture facilities in the Northwestern region of the Russian Federation, as well as in several foreign countries. Eye lesions lead to decline in immunophysiological state and growth rates in aquaculture, reduction in the number of healthy fish, increased feed costs, and release of substandard fish from hatcheries into natural water bodies, sometimes resulting in their mortality. Basic information on factors contributing to the development of ocular pathologies in salmonids is presented.
An analys is of therapeutic and preventive measures for eye lesions is provided, highlighting the importance of a differentiated and causative factor-dependent approach.
Conclusion. In global veterinary practice and fish pathology, the problem of eye protrusion in fish remains understudied, with limited research on the topic. This review analyzes and differentiates the key factors contributing to the development of ocular pathologies in salmonids. Identifying these factors will enable early diagnosis, determination, and development of preventive measures or effective treatment regimens, ultimately preserving fish health, improving the productive capacities of aquaculture establishments, and reducing economic losses.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES | PORCINE DISEASES
Introduction. In Burundi, where 80% of the population are engaged in livestock farming, industries with short reproduction cycles (pig farming, poultry farming) prevail. Despite government support measures and annually increasing pig population, the country has been unable to fully meet the demand for livestock products. This is due to numerous problems in the sector, with infectious animal diseases being the primary issue. Infectious disease outbreaks can have catastrophic consequences for the human population, including threats to food security, loss of access to animal protein, increased production costs due to the need for expensive disease control measures, and risks to human health in case of zoonotic diseases.
Objective. The aim is to study the nosological profile of porcine infectious diseases, identify factors contributing to animal infections and assess the swine erysipelas epizootic situation in the Republic of Burundi from 2018 to 2023.
Materials and methods. Data of annual reports of the General Directorate of Animal Health and test results of the National Veterinary Laboratory of Burundi (2018–2023) were used to analyze the epizootic situation on infectious porcine diseases. Retrospective and epizootiological analyses were conducted and variational statistical methods were applied.
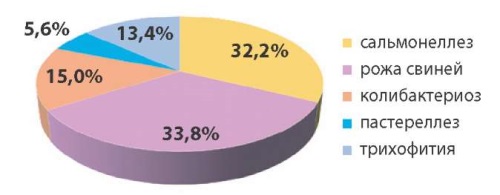
Results. The analysis revealed a high prevalence of porcine parasitic diseases, which is attributed to the equatorial climate. Within the overall structure of infectious diseases, parasitic infestations ranked first, growing from 81.2% in 2018 to 92.8% in 2023. Bacterial infections were the second most widespread, rising from 3.6% in 2018 to 6.3% in 2023. A steady increase in swine erysipelas cases was observed: in 2023 the number of cases was 1.7 times higher than in 2022 and seven times higher than in 2020. Moreover, the number of provinces where the disease is detected is annually growing. Swine erysipelas is currently reported in 12 out of 18 Burundian provinces.
Conclusion. The Republic of Burundi suffers significant annual losses due to animal deaths caused by infectious disease outbreaks. In the absence of specific disease prevention measures (particularly for erysipelas) and weak veterinary control of animal movements between households, infections spread rapidly. Therefore, studying the epizootic situation and developing measures to stabilize it under local conditions is a crucial scientific and practical task for ensuring biological and food security.
Introduction. The most effective strategy to control African swine fever is to implement a set of anti-epizootic measures aimed at preventing introduction and spread of the disease pathogen. Currently, there is a wide range of commercially available disinfectants used at the facilities subject to veterinary control. Their effectiveness against African swine fever virus is unknown and is only confirmed by the manufacturers, who do not always provide substantiated evidence.
Objective. The objective of the research is to test virucidal activity of various disinfectants against African swine fever pathogen in the laboratory.
Materials and methods. Twelve samples of disinfectants with different chemical compositions were tested. The first in vitro assessment stage was carried out using suspension method, i.e. working solutions of the tested disinfectants in experimental concentrations and exposure times were added to the liquid-phase virus-containing material. During the second stage, swabs from concrete test plates contaminated with African swine fever virus were tested following treatment of surfaces with the working disinfectant solutions. Each stage was performed in two variants: without organic contamination and with its imitation (application of inactivated bovine serum on the test surface). The samples were tested using virus isolation in a sensitive porcine spleen cell culture. Results were assessed and interpreted in hemadsorption test. The disinfectant sample was considered to exhibit virucidal activity, if no reproduction of African swine fever virus was observed.
Results. Nine out of twelve tested disinfectants demonstrated a virucidal effect against reference African swine fever virus Arm 07 strain (genotype II), when tested on test surfaces. Such results suggest the need to evaluate further the efficacy of various disinfectants against this pathogen.
Conclusion. The fact that such disinfectant products that are incapable of inactivating African swine fever virus under the conditions specified in their instructions are potentially marketed underlines the need to improve regulatory framework in order to ensure effectiveness of general disease prevention and control measures.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES | BOVINE DISEASES
Introduction. Non-specific tuberculin reactions are among the most critical challenges in tuberculosis diagnosis, with their incidence increasing annually. Given the complex epidemiological challenges, improving bovine tuberculosis diagnostics is critically important.
Objective. Development of effective comprehensive differential bovine tuberculosis diagnosis and introduction of improved techniques for the infection detection in farms with different animal health statuses in the Republic of Dagestan.
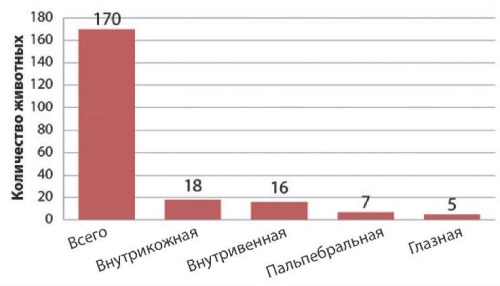
Materials and methods. 1,670 cattle were subjected to tuberculin testing; 3,502 serum samples were used for serological testing, 112 samples for immunological testing, 57 samples of pathological material collected from animals and 76 environmental samples were used for bacteriological testing. Mycobacterium bovis, Mycobacterium bovis BCG, Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium scrofulaceum strains were used in the study.
Results. Nonspecific reactions in the farms of all categories were found to be widespread in the Republic. Diagnostic value of intradermal and intravenous tuberculin tests in tuberculosis-infected herds was determined (9.4% of extra-detected diseased animals). Complement fixation test is poorly sensitive and highly specific. © Баратов М. О., 2025
Indirect haemagglutination assay results are not confirmed by conventional methods in most cases, which suggests their low specificity. 39 mycobacterial isolates were recovered from 57 biological samples and identified: 8 (20.5%) as M. bovis; 31 (79.5%) as non-tuberculous mycobacteria (acid-fast species), among them 29 (93.5%) were identified as Runyon II organisms, 2 (6.5%) as Runyon III organisms. 43 isolates out of 76 environmental samples were recovered: among them 2 (4.6%) were identified as Mycobacterium bovis, 23 (53.5%) as Runyon II organisms and 18 (41.9%) as Runyon III organisms. Among culture media, Löwenstein- Jensen’s egg-based medium provides the best growth performance and most effective suppression of competing microflora.
Conclusion. The obtained data provide a fundamental basis for developing an effective comprehensive method for differential diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis.
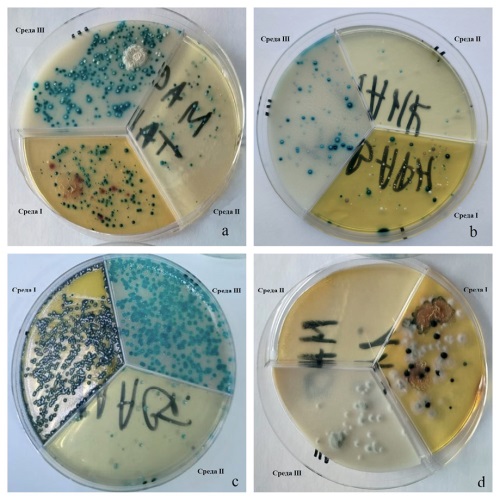
Introduction. Bovine mastitis remains one of the most prevalent and economically significant diseases in dairy cattle production. Three chromogenic media have been proposed for the diagnosis, each specifically designed for isolation and differentiation of certain mastitis pathogen groups: Medium I is intended for Enterobacteriaceae family bacteria, Medium II – for Staphylococcus genus microorganisms, Medium III – for Streptococcus genus bacteria.
Objective. The objective is to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, differentiation capacities and inhibitory properties of these chromogenic media, and to test the media using milk samples from mastitic cows.
Materials and methods. For sensitivity testing, the control strains (Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli) at concentrations of 1×100, 1×101, and 1×102 CFU/mL were used. Microbial growth was assessed following 24-hour incubation at 37 °C. Specificity and differentiation capacities were studied using 22 microbial strains, their growth patterns and colony coloration in chromogenic and control media were compared. Inhibitory properties were determined based on presence/absence of culture growth. The media were evaluated using milk samples from mastitic cows and standardized culturing methods.
Results. The chromogenic media demonstrated sensitivity comparable to the control media (Columbia agar supplemented with 5% defibrinated sheep blood), p > 0.05. Medium I enabled reliable color-based differentiation but showed limited inhibitory effects. Medium II ensured selective isolation of staphylococci while effectively suppressing growth of other bacteria. Medium III supported growth of both enterococci and streptococci, including Streptococcus agalactiae. The tests conducted in milk samples confirmed genus level differentiation capability.
Conclusion. The developed chromogenic media ensure high-accuracy mastitis diagnosis due to their sensitivity, specificity and differentiation properties. Their implementation makes it possible to cover an extensive range of microorganisms and to selectively isolate the targeted bacterial groups. Further work will be aimed at improving the media for fungal growth suppression and increasing the diagnostic accuracy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES | DISEASES OF SMALL PETS
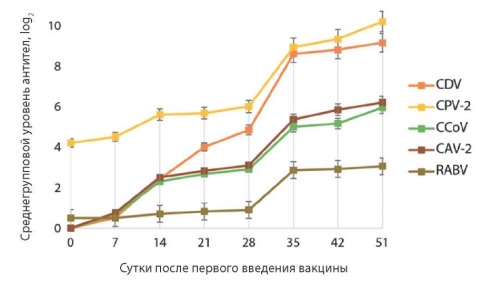
Introduction. Recently “Carnican-5R” vaccine against canine distemper, parvovirus and coronavirus enteritis, adenovirus infection and dog rabies has been developed at the Rosselkhoznadzor-subordinated Federal Center for Animal Health (FGBI “ARRIAH”, Vladimir) in accordance with the Russian Federation legislative requirements. The virus strains currently circulating and significant in the country were used for the vaccine development.
Objective. Testing of “Carnican-5R” vaccine for its antigenic properties in target animals including determination of humoral immunity development time and duration during the observation period.
Materials and methods. “Carnican-5R” combined vaccine containing two components: freeze-dried component and liquid component were used for the test. Dogs at the age of 10–12 weeks served as animal models for testing the vaccine for its antigenic properties. The antibody levels were determined with virus neutralization test, hemagglutination inhibition test and fluorescent antibody virus neutralization test.
Results. Vaccination of dogs was found to induce antibodies to the pathogens of the specified infections. Double “Carnican-5R” vaccine administration at 21-day interval induced strong humoral response by day 35 after its first administration and an increase in the antibody titers to canine distemper – by 8.6 times, to canine parvovirus type 2 – by 2.1 times, to canine coronavirus – by 5.0 times, to canine adenovirus serotype 2 – by 5.36 times, to the rabies virus – by 5.72 times. The specific immunity lasted for at least 12 months and virus-specific antibodies titers to the pathogens remained at the protective levels.
Conclusion. “Carnican-5R” vaccine is safe and non-reactogenic for target animals and induces strong immunity in dogs that lasts for at least 12 months from the date of booster vaccination.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES | VETERINARY MICROBIOLOGY
Introduction. When the body resistance-associated compensatory mechanisms are impaired or evolutionarily developed microbiocenoses are changed the quorum sensing signaling molecules facilitates excessive growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Antibacterial potential of inhibitors of intercellular communication molecule synthesis is achieved through reducing the microorganism adhesion and, consequently, in vivo and in vitro contamination.
Objective. Study of the dynamics of morphometric and densitometric parameters of biofilms formed by Escherichia coli, Escherichia albertii, Proteus vulgaris isolates identified in poultry with respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases.
Materials and methods. Dynamics of the biofilms formed by reference strains and isolates recovered from pathological samples from ROSS-308 chickens at the age of 40–42 weeks (n = 20) were studied. The sample optical densities were determined using Immunochem-2100 photometric analyzer (HTI, USA), wavelength 580 nm (OD580). Morphometric parameters were recorded at ≥ 90.0% reliable frequency in the field of view of Н604 Trinocular Unico optical microscope (United Products & Instruments Inc., USA) and Hitachi TM3030 Plus scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan).
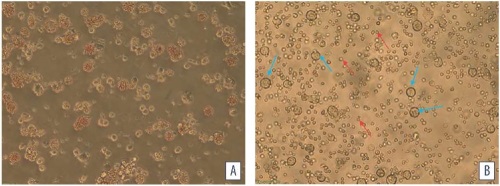
Results. Escherichia coli, Escherichia albertii, and Proteus vulgaris were isolated from pathological samples from the poultry with catarrhal hemorrhagic aerosacculitis, hemorrhagic enteritis, fibrinous polyserositis and splenomegaly signs and then identified. Direct correlations (r = 0.91) between morphometric and densitometric parameters depending on the cultivation time were established. Cells with defective cell walls, spheroplasts, needle-like and giant structures as well as revertant cells dominated during heterogeneous population dispersion.
Conclusion. General patterns of the heterogeneous microorganism population development are mediated by adhesion, synthesis of exocellular molecules, intensive cell proliferation and differentiation depending on the cell cycle stage.
Introduction. Clostridial infections, though relatively sporadic, are globally ubiquitous and specified by high mortality rates, resulting in substantial economic losses to agriculture. In cattle, pathogenic сlostridia cause diseases such as enterotoxemia, malignant edema, tetanus, and botulism. The most clinically significant species include Clostridium septicum, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium chauvoei, Clostridium novyi, and Clostridium sordellii.
Objective. Study of Clostridium spp. diversity by examination of autopsy samples and sections of cattle from different regions of Russia; determination of their anatomical localization as well as antibiotic resistance of Clostridium perfringens to the most common groups of antibiotics.
Materials and methods. Throughout the study, we adhered to internationally recognized regulatory frameworks and methodological guidelines, employing standardized microbiological and mass-spectrometric methods. Antibiotic resistance was tested against multiple drug groups, such as macrolides, monobactams, penicillins, polypeptides, glycopeptides, aminoglycosides, carbapenems, lincosamides, tetracyclines, ansamycins, diaminopyrimidines, fusidic acid derivatives, etc. Clostridium isolates were recovered and identified using routine bacteriological methods coupled with MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry.
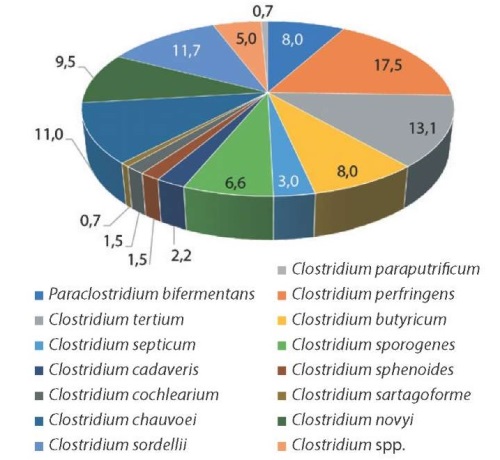
Results. Analysis of 359 biological samples resulted in isolation and identification of 137 Clostridium isolates (Paraclostridium bifermentans, Clostridium perfringens,
Clostridium tertium, Clostridium butyricum, Clostridium septicum, Clostridium sporogenes, Clostridium cadaveris, Clostridium sphenoides, Clostridium cochlearium, Clostridium sartagoforme, Clostridium chauvoei, Clostridium novyi, Clostridium sordellii, Clostridium paraputrificum, Clostridium spp.), of which 25 exhibited pathogenic potential and 17 demonstrated toxigenic properties. Сlostridia were most frequently isolated from the liver, small and large intestinal segments, and muscular tissues. Herewith, Clostridium perfringens prevailed (17.5%). This bacterium isolates demonstrated multiple drug resistance to cefixime, fusidic acid, cefotaxime, cefaclor, spectinomycin, piperacillin, clarithromycin, doripenem and doxycycline.
Conclusion. The obtained results can be used for modification of current clostridial infection treatment protocols, reformulation of immunobiological products, development of evidence-based guidelines for use of antibiotics in livestock production to mitigate antimicrobial resistance risks.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES | GENERAL ISSUES
Introduction. Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites of various fungi. The contamination with mycotoxins is subject to control. Pursuant to the accepted classification in accordance with Council Directive 96/23/EC they belong to group B3: “Other substances and environmental contaminants”. Information on detected exceedances of maximum permitted levels in feed and food is notified to the RASFF and ACN information systems, which operate across the European Union.
Objective. Analysis of RASFF and ACN notifications for mycotoxins in food and feed in 2020–2022.
Materials and methods. 1,335 publications on exceedances of maximum permitted levels of mycotoxins (aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone and patulin) in food and feed have been analysed.
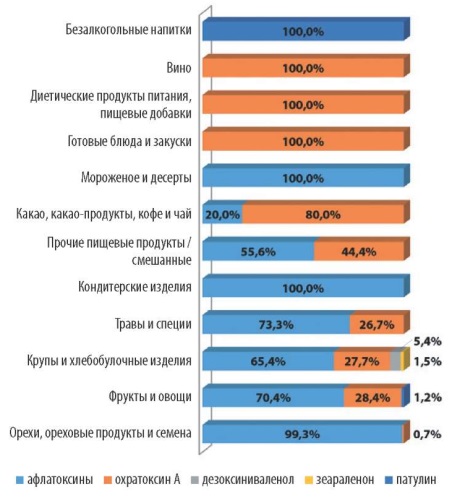
Results. Breakdown of mycotoxin notifications during the analyzed period was as follows: aflatoxins – 87.1%, ochratoxin A – 11.6%, patulin – 0.6%, deoxynivalenol – 0.5%, zearalenone – 0.2%. Aflatoxin contaminations were most often reported in groundnuts (764 notifications), ochratoxin A in dried figs (43 notifications), patulin in apple juice (6 notifications), zearalenone and deoxynivalenol in cereals and bakery products. Feedstuffs and feed ingredients were found to be contaminated only with aflatoxins (33 notifications), and 66.7% of notifications accounted for groundnuts intended for feeding. An analysis of mycotoxin contamination dynamics demonstrated that there was an increase in the number of notifications in 2021 and 2022.
Conclusion. According to RASFF and ACN notifications, mycotoxins were the third most notified hazard category in 2020–2022. Elevated mycotoxin concentrations were detected exclusively in plant products.
ANNIVERSARY DATES
COLLEAGUES’ COMMEMORATION
ISSN 2658-6959 (Online)