Перейти к:
Идентификация и некоторые биологические свойства изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus, выделенных из толстого отдела кишечника птицы
https://doi.org/10.29326/2304-196X-2025-14-3-302-309
Аннотация
Введение. Проведенная за последнее десятилетие перепись филогенетического разнообразия бактерий, колонизирующих кишечный тракт клинически здоровой птицы, показывает, что до 60% родóв, присутствующих в микробиоме кишечника, содержат спорообразующие бактерии, и эти роды составляют 30% от общей кишечной микробиоты. Были зарегистрированы преимущества, связанные с использованием пробиотиков, содержащих спорообразующие бактерии рода Bacillus. Анализ широты распространения гемолитической и потенциальной биопленкообразующей активности, а также антибиотикорезистентности у кишечной популяции споробиоты птицы необходим для понимания истинной роли аэробных спорообразователей рода Bacillus в экологии кишечного микробиома птицы.
Цель работы. Идентификация и исследование биологических характеристик (гемолитическая активность, потенциальная способность к биопленкообразованию и антибиотикорезистентность) изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus, выделенных из толстого отдела кишечника птицы.
Материалы и методы. Выделение спорообразующих бактерий из содержимого слепых отростков толстого кишечника птицы проводили путем прогревания образцов. Фенотипическую идентификацию изолятов осуществляли с использованием биохимических тест-панелей API 50CHB (bioMérieux, Франция). Гемолитические свойства определяли на колумбийском агаре (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) с добавлением 5% стерильной дефибринированной крови барана; каталазную активность – в тесте с 10%-й перекисью водорода по ОФС.1.7.2.0012.15; чувствительность к антибиотикам – диско-диффузионным методомсостандартными дисками, импрегнированными антибиотиками вконцентрациях от5до 30 μg/disk. Скрининг спорообразующих бактерий – продуцентов биопленки проводили качественным методом на сердечно-мозговом агаре (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) с добавлением индикатора конго красного и 5% сахарозы.
Результаты. Установлено, что кишечная популяция аэробной споробиоты слепых отростков толстого кишечника птицы представлена видами B. licheniformis, B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens, B. mycoides, B. megaterium и B. сereus. Все изученные изоляты были каталазоположительными, не обладали α-гемолитической активностью. У части изолятов отмечена β-гемолитическая активность. Подавляющее большинство изолятов относились к биопленкообразующим фенотипам и проявляли чувствительность к тестируемым антибиотикам.
Заключение. Вегетативные формы спорообразующих бактерий рода Bacillus потенциально могут сохраняться в сложной экосистеме кишечника или временно ассоциироваться с ней. Гемолитически активные кишечные изоляты спорообразующих бактерий не могут считаться безопасными до выяснения действия этого фактора вирулентности на организм животных. Результаты исследований могут быть использованы при отборе кандидатных штаммов бактерий рода Bacillus, выбранных в качестве пробиотиков.
Для цитирования:
Малик Н.И., Чупахина Н.А., Русанов И.А., Малик Е.В., Маленкова Л.А., Самохвалова Н.С., Сурогин М.В. Идентификация и некоторые биологические свойства изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus, выделенных из толстого отдела кишечника птицы. Ветеринария сегодня. 2025;14(3):302-309. https://doi.org/10.29326/2304-196X-2025-14-3-302-309
For citation:
Malik N.I., Chupahina N.A., Rusanov I.A., Malik E.V., Malenkova L.A., Samokhvalova N.S., Surogin M.V. Identification and some biological characteristics of Bacillus strains isolated from poultry large intestine. Veterinary Science Today. 2025;14(3):302-309. https://doi.org/10.29326/2304-196X-2025-14-3-302-309
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Микробиота кишечника играет важную роль в поддержании здоровья хозяина, поскольку она может обеспечивать организм различными питательными веществами, регулировать энергетический баланс и иммунный ответ, а также защищать от патогенов. Восстановление и поддержание стабильности кишечной микробиоты с помощью полезных бактерий было предложено в качестве потенциальной стратегии для предотвращения нежелательных последствий для здоровья кишечника взамен применения антибиотиков [1].
Проведенная за последнее десятилетие перепись филогенетического разнообразия бактерий, идентифицированных в кишечном тракте здоровой птицы, показывает, что до 60% родóв, присутствующих в микробиоме кишечника, содержат спорообразующие бактерии, и эти роды составляют 30% от общей кишечной микробиоты [2][3].
В исследованиях микробиома спорообразующие бактерии предложено рассматривать как отдельную функциональную группу в составе глобальной микробиоты. Для обозначения всей совокупности спорообразующих бактерий в микробной популяции был предложен термин sporobiota [4].
Эндоспоры образуются у представителей Firmicutes – большого, разнообразного и морфологически сложного типа бактерий [5]. В рамках этого типа представители семейства Bacillaceae рода Bacillus привлекают пристальное научное внимание, поскольку охватывают наиболее значимые для модуляции кишечной микробиоты виды [6].
Спорообразующие бактерии рода Bacillus чаще ассоциированы с почвенным микробиомом [7], а их присутствие в кишечнике связывают с употреблением кормов и воды. При этом априори считается, что бактерии рода Bacillus попадают в кишечник в споровой форме [8]. Однако накопленные данные свидетельствуют о том, что некоторые виды рода Bacillus рассматривают как микроорганизмы с бимодальным жизненным циклом, которые растут и образуют споры как в окружающей среде, так и в желудочно-кишечном тракте [9][10].
Спорообразующие бактерии рода Bacillus широко применяют в кормах для животных для улучшения роста животных и ингибирования патогенов [11][12]. Механизмы пробиотического действия микроорганизмов этого рода связаны с синтезом антимикробных веществ и молочной кислоты [13], укреплением неспецифического иммунитета [14], высвобождением ферментов амилазы, липазы, протеазы, пектиназы и целлюлазы [15]. Bacillus subtilis стимулирует рост нормальной микрофлоры кишечника, увеличивает разнообразие кишечного микробиома [16], модулирует реактивность регуляторных систем для обновления эпителия кишечника и активность иммунных клеток [17] и нейтрализует негативное влияние различных факторов, особенно антибиотикотерапии [18][19].
Также было показано, что B. subtilis играет важную роль в стимулировании развития кишечно-ассоциированной лимфоидной ткани и что именно споруляцию живых бацилл считают критически важной для этого процесса [20][21].
Выживаемость и колонизацию в пищеварительном тракте считают необходимыми факторами функциональности и проявления физиологических функций микробиоты [22]. В этом аспекте важным условием для колонизации кишечника спорообразующими бактериями является прилипание спор к слизистой оболочке кишечника и дальнейшее формирование биопленок, при котором планктонные клетки переходят в прикрепленные формы [21][23].
Термин «биопленка» используют для описания структурированного сообщества бактериальных клеток, заключенных в полимерный внеклеточный матрикс собственного производства, который прилипает к инертной или живой поверхности [24]. Полимерный внеклеточный матрикс представляет собой сложную систему, состоящую из экзополисахаридов, белка TasA, липидов, нуклеиновых кислот и различных гетерополимеров, секретируемых микроорганизмами во внеклеточную среду [25]. Проведенные исследования показали, что белок TasA и экзополисахарид являются основными компонентами биопленки. TasA – это амилоидный белок, который, как было установлено, участвует в формировании матрикса биопленки микроорганизмами, включая и спорообразующие бактерии [26-29].
Бактериальные биопленки могут защищать бактерии от воздействия окружающей среды, иммунного ответа хозяина, противомикробных средств и антибиотиков [30].
Устанавливать наличие способности у бактерий синтезировать амилоиды с помощью красителя конго красного было предложено D. J. Freeman et al. для выявления образующих слизь или биопленку Staphylococcus sp. [31]. Метод основан на морфологии и цвете колоний Staphylococcus, образующих и не образующих биопленки на агаре с конго красным. В дальнейших исследованиях была установлена возможность использования данного метода для выявления потенциальных биопленкообразователей среди широкого круга грамположительных и грамотрицательных микроорганизмов, в том числе и спорообразующих бактерий рода Bacillus [32-34].
Недавние данные свидетельствуют о том, что в биопленках протекает более активный процесс споруляции Bacillus, чем у планктонных клеток [35].
Возросшая угроза распространения антибиотикорезистентных вариантов патобионтов выдвигает на первый план направление исследований по оценке антибиотикорезистентности комменсальной кишечной микробиоты как потенциальных доноров детерминант резистентности.
В свете этой проблемы было высказано предположение, что спорообразующие бактерии могут иметь важное значение в распространении и накоплении генов устойчивости к антибиотикам из-за их способности противостоять лечению антибиотиками [36, 37]. Однако степень устойчивости к антибиотикам и способности к биопленкообразованию у представителей кишечной споробиоты по сути неизвестна.
Предыдущие исследования распространения устойчивости к антибиотикам и способности к формированию биопленок бактерий рода Bacillus были сосредоточены на небольшом количестве бактерийных видов и не охватывали изоляты, выделенные из кишечной микробиоты птицы [38-41].
По-прежнему остается недостаточно изученной широта распространения гемолитической активности в кишечной популяции аэробных бактерий рода Bacillus и роль их гемолизинов в поддержании целостности слизистой кишечника и не установлено, что продукция гемолизинов не причиняет вреда хозяину. Негемолитические (γ-гемолитические) штаммы, как правило, считают безопасными для их хозяев, в то время как штаммы с гемолитической активностью считают патогенными [42][43].
Учитывая современную концепцию о значении кишечной микробиоты в поддержании колонизационной резистентности кишечника, этот пробел в знаниях приводит к отсутствию понимания истинной роли аэробных спорообразователей рода Bacillus в кишечной микробиоте птицы, специфичности в выборе и применении их в качестве пробиотиков [44][45].
Актуальность работы заключается в том, что оценка безопасности аэробных спорообразующих бактерий рода Bacillus, которые широко используются в технологии производства пробиотических кормовых добавок, связана не только с видовой идентификацией, но и с индивидуальными особенностями штаммов.
Новизна полученных данных состоит в том, что, оценивая перспективы использования бактерий рода Bacillus для создания пробиотических кормовых добавок, изучены некоторые биологические свойства изолятов, выделенных из слепых отростков толстого отдела кишечника промышленной птицы.
Цель работы – исследование биологических свойств изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus (гемолитическая активность, потенциальная способность к биопленкообразованию и антибиотикорезистентность), выделенных из толстого отдела кишечника птицы с целью отбора штаммов, перспективных для использования в биотехнологии получения пробиотических продуктов.
Материалы и методы
Спорообразующие бактерии, использованные в исследовании, были выделены из образцов содержимого слепых отростков толстого кишечника клинически здоровой птицы, полученной из хозяйств Московской области, благополучных по инфекционным заболеваниям. Птицу в виварии усыпляли с помощью CO2 и вскрывали общепринятым методом. Все манипуляции с животными соответствовали этическим стандартам, принятым Европейской конвенцией ETS № 123.
Слепые отростки толстого кишечника изолировали путем наложения лигатур на границе с прямой кишкой, отсекали, помещали в отдельную емкость и переносили в лабораторию с соблюдением холодовой цепи 2–8 °С. Не позднее 30 мин после получения изолированных отростков содержимое каждого выдавливали в стерильную одноразовую посуду и маркировали. Полученные аликвоты каждого образца химуса разводили забуференной пептонной водой в соотношении 1:100, ресуспендировали интенсивным перемешиванием до получения равномерной суспензии.
Для изоляции спорообразующих бактерий аликвоты прогревали на водяной бане при 65 °C в течение 45 мин [46].
Для получения изолированных колоний прогретые аликвоты штриховым посевом высевали на триптон-соевый агар (SCD-агар; HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия). Культивировали в аэробных условиях при (37 ± 1) °С. Просмотр посевов проводили через 18, 24 и 36 ч культивирования.
Отбирали колонии, имеющие морфологические признаки бактерий рода Bacillus, и очищали повторным высевом на SCD-агар. Через 18 и 24 ч культивирования после визуальной оценки степени роста и микроскопии мазков, окрашенных по Граму, изоляты спорообразующих бактерий пересевали на SCD-бульон (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) и бульонные культуры вегетативных клеток использовали в работе.
Фенотипическая характеристика. Была проведена фенотипическая характеристика изолятов спорообразующих бактерий по морфологическим признакам, окрашиванию по Граму, гемолитической активности, каталазной активности, способности к биопленкообразованию и чувствительности к антибиотикам. Все тесты осуществляли в двух повторностях.
Идентификация изолятов. Фенотипическую идентификацию изолятов спорообразующих бактерий проводили с использованием коммерческих биохимических диагностических тест-панелей одноразового пользования API 50CHB (bioMérieux, Франция). Этот тест позволяет классифицировать бактериальные штаммы в соответствии с их способностью ферментировать 49 различных углеводов. Результаты анализировали с помощью программного обеспечения APIWEB™ (bioMérieux, Франция).
Тест на гемолитическую активность. Гемолитические свойства изолятов спорообразующих бактерий определяли с использованием колумбийского агара (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) с добавлением 5% стерильной дефибринированной крови барана. Суточные культуры изолятов спорообразующих бактерий уколом высевали на поверхность агара. Учет реакции проводили через 24 ч после инкубации при (37 ± 1) °С. Изолят считали α-гемолитическим, когда колонии вызывали зеленое или коричневое изменение цвета окружающей среды, β-гемолитическим, когда истинный лизис эритроцитов приводил к образованию чистой, прозрачной зоны, окружающей колонии, и γ-гемолитическим, или негемолитическим, когда в окружающей среде не наблюдалось реакции [47].
Тест на каталазу. Каталазную активность бактериальных изолятов определяли в тесте с 10%-й перекисью водорода [48]. Выделение кислорода, заметное по образованию пузырьков газа, свидетельствует о продукции каталазы.
Тест на чувствительность к антибиотикам. Тест на чувствительность к антибиотикам изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus проводили диско-диффузионным методом [49]. Использовали стандартные диски, импрегнированные следующими антибиотиками в концентрациях от 5 до 30 μg/disk (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия): ципрофлоксацином (Cip 5), рифампицином (Rif 5), энрофлоксацином (Ex5), доксициклином (Do10), гентамицином (Gen10), неомицином (N30), цефазолином (Cz30), норфлоксацином (Nx10), бензилпенициллином (P100), пефлоксацином (Pf5), канамицином (K30), линкомицином (L15), азитромицином (AZM15), налидиксовой кислотой (NA30), хлорамфениколом (C30), окситетрациклином (O30), имипенемом (Ipm10), олеандомицином (Ol15), клиндамицином (Cd2), кларитромицином (Clr15), оксациллином (Ox1), ампициллином (Amp25).
Агаровые 18-часовые бактериальные культуры спорообразующих бактерий доводили по стандарту МакФарланда до 0,5 ед. оптической плотности, втирали 250 мкл культуры в поверхность SCD-агара и расставляли с помощью диспенсера (HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) диски с антибиотиками по 8 шт. на чашку, затем помещали в термостат при (37 ± 1) °С на 20–24 ч.
Штаммы обозначались как резистентные (R), если концентрация указанных в документах EFSA (Европейское агентство по безопасности продуктов питания) антибиотиков превышала пороговый уровень для штаммов Bacillus [50]. Из-за отсутствия достоверных интерпретирующих документов для ряда антибиотиков штаммы Bacillus, образующие зоны ингибирования вокруг диска с антибиотиком менее 12 мм, считали устойчивыми к антибиотикам.
Определение продуцентов биопленки. Скрининг спорообразующих бактерий – потенциальных продуцентов биопленки – проводили качественным методом путем обнаружения внеклеточных амилоидных белков на сердечно-мозговом агаре (BHI-агар, HiMedia Laboratories Pvt Ltd., Индия) с добавлением индикатора конго красного и 5% сахарозы [31].
Испытуемую суточную бульонную культуру засевали уколом на BHI-агар с конго красным и помещали в термостат на 48 ч инкубации при температуре (37 ± 1) °C. При просмотре визуально оценивали цвет и морфологию выросших колоний испытуемого изолята.
При взаимодействии конго красного с амилоидными белками биопленки образуется продукт, который придает колониям или темно-красный, или темно-коричневый цвет с черным основанием. Слабые продуценты биопленки обычно остаются розовыми, хотя иногда может наблюдаться потемнение в центре колоний. Изоляты, не способные формировать биопленку, образуют колонии белого или очень светло-розового цвета [51].
Результаты и обсуждение
При проведении исследования всего было выделено и идентифицировано до уровня вида 68 штаммов аэробных спорообразующих бактерий рода Bacillus.
Фенотипические данные подтвердили принадлежность изолятов, выделенных из содержимого слепых отростков толстого отдела кишечника клинически здоровой птицы, к спорообразующим бактериям.
Идентифицированные изоляты спорообразующих бактерий были представлены 5 видами: Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis/amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus mycoides. Ряд изолятов не поддавался идентификации по стандартизованной системе API 50CHB.
Микроскопическое исследование выделенных клеток показало наличие разнообразной коллекции палочковидных бактерий, продуцирующих эндоспоры различных размеров и форм.
Колонии спорообразующих бактерий отличались широким полиморфизмом. Изоляты B. licheniformis через 18–24 ч роста на SCD-агаре образовывали приподнятые среднего размера колонии, окрашенные в белый или бежевый цвет, в форме цветка.
При посеве на SCD-агар изолятов B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens через 18–24 ч вырастали крупные белые, среднего размера с более светлой точкой в центре или шероховатые волнистые колонии бело-кремового цвета сухой мелкоморщинистой структуры, слегка приподнятые над поверхностью агара.
Изоляты B. megaterium на SCD-агаре образовывали резко окаймленные колонии грязно-белого цвета.
В морфологическом отношении колонии изолятов B. mycoides и B. cereus были идентичными и имели вид шероховатых, расплывающихся, ризоидных серо-белого цвета колоний с волнистыми краями или морщинистых молочного цвета колоний с волнистыми краями.
Выделенные изоляты спорообразующих бактерий были оценены на предмет их безопасности по гемолитической активности (табл. 1).
Все изоляты спорообразующих бактерий, выделенных из образцов химуса слепых отростков кишечника цыплят, не обладали α-гемолической активностью. У 14 из 57 исследованных изолятов видов B. licheniformis, B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens, B. megaterium и B. cereus при росте на кровяном агаре наблюдали широкую зону гемолиза, характерную для β-гемолитических бактерий (рис. 1). Было обнаружено, что 9 изолятов спорообразующих бактерий обладают γ-гемолитической активностью.
Большинство изученных изолятов спорообразующих микроорганизмов, выросших на BHI-агаре с конго красным, по окраске колоний темно-красного цвета с черным основанием были отнесены к потенциальным образователям биопленок, за исключением 3 изолятов B. licheniformis, 1 изолята B. megaterium и 2 изолятов B. cereus, образующих светлые розовые колонии (рис. 2).
Тесты на чувствительность к антибиотикам показали, что большая часть изученных изолятов спорообразующих бактерий были чувствительны ко всем 22 исследованным антибиотикам (табл. 2).
Только 4 изолята спорообразующих бактерий были резистентны к рифампицину, 7 – к цефазолину, 12 – к линкомицину, 6 – к окситетрациклину. Некоторые изоляты оказались резистентными к 2 антибиотикам, но большинство изолятов проявляли резистентность не более чем к одному антибиотику.
Таблица 1
Гемолитическая активность и признак биопленкообразования у изолятов спорообразующих бактерий, выделенных из слепых отростков кишечника птицы
Table 1
Hemolytic activity and biofilm-forming capacity of spore-forming bacterial isolates from poultry cecal appendages
|
Видовая принадлежность изолята по стандартизованной системе API 50CHB |
Всего изолятов |
Количество гемолитически активных изолятов |
Количество изолятов – потенциальных продуцентов биопленки |
||
|
тип гемолиза |
|||||
|
α |
β |
γ |
|||
|
B. licheniformis |
26 |
0 |
4 |
6 |
23 |
|
B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens |
16 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
16 |
|
B. megaterium |
3 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
B. mycoides |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
|
B. cereus |
7 |
0 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
Неидентифицируемые виды |
11 |
0 |
5 |
4 |
не исследовали |
|
Итого |
68 |
0 |
19 |
13 |
51 |
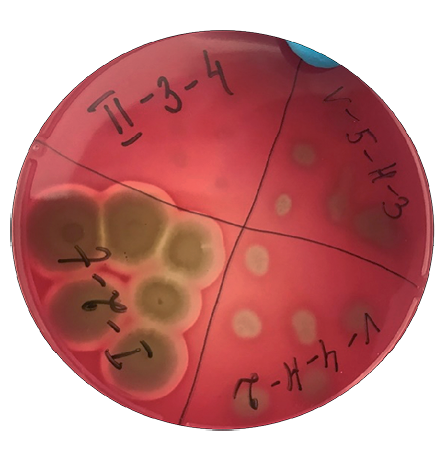
Рис. 1. Гемолитическая активность изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus, выращенных на SCD-агаре с добавлением крови барана при (37 ± 1) °С в течение 24 ч
Fig. 1. Hemolytic activity of Bacillus isolates cultured on sheep blood-supplemented SCD agar at (37 ± 1) °C for 24 hours

Рис. 2. Изоляты бактерий рода Bacillus, инкубированные на BHI-агаре с конго красным при (37 ± 1) °С в течение 24 ч
Fig. 2. Bacillus isolates cultured on Congo red-supplemented BHI agar at (37 ± 1) °C for 24 hours
Таблица 2
Профили чувствительности 57 спорообразующих изолятов к антибиотикам, определенные диско-диффузионным методом
Table 2
Antibiotic sensitivity profiles of 57 spore-forming isolates determined using disk diffusion method
|
№ п/п |
Тип диска с антибиотиком |
Количество чувствительных к антибиотику изолятов |
||||
|
B. licheniformis (n = 26) |
B. subtilis/ amyloliquefaciens (n = 16) |
B. megaterium (n = 3) |
B. mycoides |
B. cereus |
||
|
1 |
Ципрофлоксацин (5 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
2 |
Рифампицин (5 μg/disk) |
2 |
1 |
1 |
+ |
+ |
|
3 |
Энрофлоксацин (5 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
4 |
Доксициклин (10 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
5 |
Гентамицин (10 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
6 |
Неомицин (30 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
7 |
Цефазолин (30 μg/disk) |
3 |
+ |
1 |
+ |
3 |
|
8 |
Норфлоксацин (10 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
9 |
Бензилпенициллин (100 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
10 |
Пефлоксацин (5 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
11 |
Канамицин (30 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
1 |
+ |
|
12 |
Линкомицин (15 μg/disk) |
8 |
3 |
1 |
+ |
+ |
|
13 |
Азитромицин (15 μg/disk) |
+ |
2 |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
14 |
Налидиксовая кислота (٣0 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
15 |
Хлорамфеникол (30 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
16 |
Окситетрациклин (30 μg/disk) |
2 |
2 |
+ |
1 |
1 |
|
17 |
Имипенем (10 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
18 |
Олеандомицин (15 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
19 |
Ампициллин (2٥ μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
20 |
Клиндамицин (2 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
21 |
Кларитромицин (15 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
22 |
Оксациллин (1 μg/disk) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Заключение
По результатам исследований идентифицированные виды спорообразующих бактерий рода Bacillus, выделенные из слепых отростков кишечника промышленной птицы, включали: B. licheniformis, B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens, B. mycoides, B. megaterium и B. cereus, ряд изолятов не поддавался идентификации.
Все изученные изоляты были каталазоположительными, не обладали α-гемолитической активностью. У части изолятов отмечена β-гемолитическая активность, что не позволяет рассматривать их как непатогенные.
Дополнительно была исследована потенциальная способность выделенных изолятов к биопленкообразованию, что косвенно характеризует возможность их выживания в кишечнике. Подавляющее большинство изолятов относились к потенциальным биопленкообразующим фенотипам и проявляли чувствительность к 22 тестируемым антибиотикам.
Гемолитически активные кишечные изоляты спорообразующих бактерий не могут считаться безопасными до выяснения действия этого фактора вирулентности на организм животных.
Результаты исследований могут быть использованы при отборе кандидатных штаммов бактерий рода Bacillus, выбранных в качестве пробиотиков.
Список литературы
1. Von Martels J. Z., Sadabad M. S., Bourgonje A. R., Blokzijl T., Dijkstra G., Faber K. N., Harmsen H. J. M. The role of gut microbiota in health and disease: in vitro modeling of host-microbe interactions at the aerobe-anaerobe interphase of the human gut. Anaerobe. 2017; 44: 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2017.01.001
2. Kearney S. M., Gibbons S. M., Poyet M., Gurry T., Bullock K., Allegretti J. R., et al. Endospores and other lysis-resistant bacteria comprise a widely shared core community within the human microbiota. The ISME Journal. 2018; 12 (10): 2403–2416. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0192-z
3. Lan P. T. N., Hayashi H., Sakamoto M., Benno Y. Phylogenetic analysis of cecal microbiota in chicken by the use of 16S rDNA clone libraries. Microbiology and Immunology. 2002; 46 (6): 371–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02709.x
4. Tetz G, Tetz V. Introducing the sporobiota and sporobiome. Gut Pathogens. 2017; 9 (1):38. https://doi:10.1186/s13099-017-0187-8
5. Elshaghabee F. M., Rokana N., Gulhane R. D., Sharma C., Panwar H. Bacillus as potential probiotics: status, concerns, and future perspectives. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2017; 8:1490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01490
6. Egan M., Dempsey E., Ryan C. A., Ross R. P., Stanton C. The sporobiota of the human gut. Gut Microbes. 2021; 13 (1):е1863134. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2020.1863134
7. Zeigler D. R., Perkins J. B. The Genus Bacillus. In: Practical Handbook of Microbiology. Ed. by L. H. Green, E. Goldman. 4th ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2021; Chapter 22: 249–278. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003099277
8. Priest F. G. Systematics and Ecology of Bacillus. In: Bacillus subtilis and Other Gram-Positive Bacteria: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Genetics. Ed. by A. L. Sonenshein, J. A. Hoch, R. Losick. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1993; Chapter 1: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555818388.ch1
9. Barbosa T. M., Serra C. R., La Ragione R. M., Woodward M. J., Henriques A. O. Screening for Bacillus isolates in the broiler gastrointestinal tract. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2005; 71 (2): 968–978. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.2.968-978.2005
10. Hoa T. T., Duc L. H., Isticato R., Baccigalupi L., Ricca E., Van P. H., Cutting S. M. Fate and dissemination of Bacillus subtilis spores in a murine model. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2001; 67 (9): 3819–3823. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.9.3819-3823.2001
11. Mohammed A. A., Zaki R. S., Negm E. A., Mahmoud M. A., Cheng H. W. Effects of dietary supplementation of a probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) on bone mass and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poultry Science. 2021; 100 (3):100906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.073
12. Abramowicz K., Krauze M., Ognik K. The effect of a probiotic preparation containing Bacillus subtilis PB6 in the diet of chickens on redox and biochemical parameters in their blood. Annals of Animal Science. 2019; 19 (2): 433–451. https://doi.org/10.2478/aoas-2018-0059
13. Леляк А. А., Штерншис М. В. Антагонистический потенциал сибирских штаммов Bacillus spp. в отношении возбудителей болезней животных и растений. Вестник Томского государственного университета. Биология. 2014; (1): 42–55. https://elibrary.ru/tgwlvz
14. Dong Y., Li R., Liu Y., Ma L., Zha J., Qiao X., et al. Benefit of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis BYS2 on growth performance, immune response, and disease resistance of broilers. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins. 2020; 12: 1385–1397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09643-w
15. Смирнов В. В., Резник С. Р., Кудрявцев В. А., Осадчая А. И., Сафронова Л. А. Внеклеточные аминокислоты аэробных спорообразующих бактерий. Микробиология. 1992; 61 (5): 865–872.
16. Wu B. Q., Zhang T., Guo L. Q., Lin J. F. Effects of Bacillus subtilis KD1 on broiler intestinal flora. Poultry Science. 2011; 90 (11): 2493–2499. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2011-01529
17. Sumi C. D., Yang B. W., Yeo I.-C., Hahm Y. T. Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: a new era for antibiotics. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 2015; 61 (2): 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0613
18. Horosheva T. V., Vodyanoy V., Sorokulova I. Efficacy of Bacillus probiotics in prevention of antibiotic‐associated diarrhoea: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. JMM Case Reports. 2014; 1 (3):e004036. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmmcr.0.004036
19. Sorokulova I. Modern status and perspectives of Bacillus bacteria as probiotics. Journal of Probiotics & Health. 2013; 1 (4):е106. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-8901.1000e106
20. Duc L. H., Hong H. A., Uyen N. Q., Cutting S. M. Intracellular fate and immunogenicity of B. subtilis spores. Vaccine. 2004; 22 (15–16): 1873–1885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.11.021
21. Lu S., Na K., Li Y., Zhang L., Fang Y., Guo X. Bacillus-derived probiotics: metabolites and mechanisms involved in bacteria – host interactions. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2024; 64 (6): 1701–1714. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2118659
22. Kubota H., Senda S., Nomura N., Tokuda H., Uchiyama H. Biofilm formation by lactic acid bacteria and resistance to environmental stress. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 2008; 106 (4): 381–386. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.106.381
23. Todorov S. D., Ivanova I. V., Popov I., Weeks R., Chikindas M. L. Bacillus spore-forming probiotics: benefits with concerns? Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 2022; 48 (4): 513–530. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2021.1983517
24. Costerton J. W., Stewart P. S., Greenberg E. P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999; 284 (5418): 1318–1322. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5418.1318
25. Branda S. S., Vik Å., Friedman L., Kolter R. Biofilms: the matrix revisited. Trends in Microbiology, 2005; 13 (1): 20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.006
26. Lasa I., Penadés J. R. Bap: a family of surface proteins involved in biofilm formation. Research in Microbiology. 2006; 157 (2): 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2005.11.003
27. Taglialegna A., Lasa I., Valle J. Amyloid structures as biofilm matrix scaffolds. Journal of Bacteriology. 2016; 198 (19): 2579–2588. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00122-16
28. Akbey Ü., Andreasen M. Functional amyloids from bacterial biofilms – structural properties and interaction partners. Chemical Science. 2022; 13 (22): 6457–6477. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC00645F
29. Cámara-Almirón J. Structural and functional study of bacterial amyloids in Bacillus subtilis: Author’s thesis. Universidad de Málaga; 2020. https://hdl.handle.net/10630/19863
30. Fazeli-Nasab B., Sayyed R. Z., Mojahed L. S., Rahmani A. F., Ghafari M., Antonius S., Sukamto. Biofilm production: a strategic mechanism for survival of microbes under stress conditions. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2022; 42:102337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102337
31. Freeman D. J., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T. New method for detecting slime production by coagulase negative staphylococci. Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1989; 42 (8): 872–874. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.42.8.872
32. Saxena N., Maheshwari D., Dadhich D., Singh S. Evaluation of Congo red agar for detection of biofilm production by various clinical Candida isolates. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2014; 3 (59): 13234–13238. https://doi.org/10.14260/jemds/2014/3761
33. Branda S. S., Chu F., Kearns D. B., Losick R., Kolter R. A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Molecular Microbiology. 2006; 59 (4): 1229–1238. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.05020.x
34. Romero D., Aguilar C., Losick R., Kolter R. Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010; 107 (5): 2230–2234. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910560107
35. Lindsay D., Brözel V. S., Von Holy A. Spore formation in Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Journal of Food Protection. 2005; 68 (4): 860–865. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-68.4.860
36. Bengtsson-Palme J., Abramova A., Berendonk T. U., Coelho L. P., Forslund S. K., Gschwind R., et al. Towards monitoring of antimicrobial resistance in the environment: For what reasons, how to implement it, and what are the data needs? Environment International. 2023; 178: 108089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2023.108089
37. Dulya O., Mikryukov V., Shchepkin D. V., Pent M., Tamm H., Guazzini M., et al. A trait-based ecological perspective on the soil microbial antibiotic-related genetic machinery. Environment International. 2024; 190:108917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2024.108917
38. BerićT., Biočanin M., Stanković S., Dimkić I., Janakiev T., Fira Đ., Lozo J. Identification and antibiotic resistance of Bacillus spp. isolates from natural samples. Archives of Biological Sciences. 2018; 70 (3): 581–588. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS180302019B
39. Adamski P., Byczkowska-Rostkowska Z., Gajewska J., Zakrzewski A. J., Kłębukowska L. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Bacillus sp. isolated from raw milk. Microorganisms. 2023; 11 (4):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041065
40. Kowalska J., Maćkiw E., Stasiak M., Kucharek K., Postupolski J. Biofilm-forming ability of pathogenic bacteria isolated from retail food in Poland. Journal of Food Protection. 2020; 83 (12): 2032–2040. https://doi.org/10.4315/JFP-20-135
41. Morikawa M. Beneficial biofilm formation by industrial bacteria Bacillus subtilis and related species. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 2006; 101 (1): 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.1
42. Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Nature and properties of a cytolytic agent produced by Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 1970; 61 (3): 361–369. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-61-3-361
43. AlGburi A., Volski A., Cugini C., Walsh E. М., Chistyakov V. А., Mazanko M. S., et al. Safety properties and probiotic potential of Bacillus subtilis KATMIRA1933 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895. Advances in Microbiology. 2016; 6 (6): 432–452. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2016.66043
44. Deng F., Chen Y., Sun T., Wu Y., Su Y., Liu C., et al. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence characteristics and genotypes of Bacillus spp. from probiotic products of diverse origins. Food Research International. 2021; 139:109949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109949
45. Похиленко В. Д., Перелыгин В. В. Пробиотики на основе спорообразующих бактерий и их безопасность. Химическая и биологическая безопасность. 2007; (2–3): 20–41. http://www.cbsafety.ru/rus/saf_32_2.asp
46. Otiniano N. M., Farfán-Córdova M., Cabeza J. G., Cabanillas-Chirinos L. Isolation and selection of spore-forming bacilli with potential for self-healing of concrete. Scientific Reports. 2024; 14:27223. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77241-9
47. Buxton R. Blood agar plates and hemolysis protocols. American Society for Microbiology. 30 September 2005. 9 p. https://asm.org/getattachment/7ec0de2b-bb16-4f6e-ba07-2aea25a43e76/protocol
48. ОФС.1.7.2.0012.15. Производственные пробиотические штаммы и штаммы для контроля пробиотиков. Государственная фармакопея Российской Федерации. XIV издание. https://pharmacopoeia.regmed.ru/pharmacopoeia/izdanie-14/1/1-7/1-7-2/proizvodstvennye-probioticheskie-shtammy-i-shtammy-dlya-kontrolya-probiotikov
49. Определение чувствительности микроорганизмов к антимикробным препаратам: рекомендации Межрегиональной ассоциации по клинической микробиологии и антимикробной химиотерапии. Версия 2021-01. https://www.antibiotic.ru/files/321/clrec-dsma2021.pdf
50. EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Guidance on the assessment of bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobials of human and veterinary importance. EFSA Journal. 2012; 10 (6):2740. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2740
51. Okouakoua F. Y., Kayath C. A., Mokemiabeka S. N., Moukala D. C. R., Kaya-Ongoto M. D., Nguimbi E. Involvement of the Bacillus SecYEG pathway in biosurfactant production and biofilm formation. International Journal of Microbiology. 2024; 2024:6627190. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/6627190
Об авторах
Н. И. МаликРоссия
Малик Нина Ивановна - д-р биол. наук, профессор, главный научный сотрудник отдела научного планирования и НИР ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
Н. А. Чупахина
Россия
Чупахина Наталия Александровна - канд. биол. наук, ведущий научный сотрудник отдела бактериологии ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
И. А. Русанов
Россия
Русанов Иван Анатольевич - старший научный сотрудник научно-технологической лаборатории ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
Е. В. Малик
Россия
Малик Евгений Васильевич - канд. вет. наук, ведущий научный сотрудник отдела научного планирования и НИР ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
Л. А. Маленкова
Россия
Маленкова Лия Андреевна - старший научный сотрудник отдела бактериологии ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
Н. С. Самохвалова
Россия
Самохвалова Надежда Сергеевна - научный сотрудник отдела бактериологии ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
М. В. Сурогин
Россия
Сурогин Михаил Витальевич - канд. вет. наук, заведующий отделом бактериологии, ФГБУ «ВГНКИ».
Звенигородское шоссе, 5, Москва, 123022
Рецензия
Для цитирования:
Малик Н.И., Чупахина Н.А., Русанов И.А., Малик Е.В., Маленкова Л.А., Самохвалова Н.С., Сурогин М.В. Идентификация и некоторые биологические свойства изолятов бактерий рода Bacillus, выделенных из толстого отдела кишечника птицы. Ветеринария сегодня. 2025;14(3):302-309. https://doi.org/10.29326/2304-196X-2025-14-3-302-309
For citation:
Malik N.I., Chupahina N.A., Rusanov I.A., Malik E.V., Malenkova L.A., Samokhvalova N.S., Surogin M.V. Identification and some biological characteristics of Bacillus strains isolated from poultry large intestine. Veterinary Science Today. 2025;14(3):302-309. https://doi.org/10.29326/2304-196X-2025-14-3-302-309
JATS XML



































